Overview
A condition where a person, male or female, has excessive hair growth on his or her body is an abnormal and strange phenomenon. Though rare, this condition can occur at birth, as an inherited condition, or evolve later, regardless of your sex, age, or race. However, there are only a few cases of this condition called werewolf syndrome since its discovery in the 15th century. This blog will give more simplified details about this hair growth disorder called hypertrichosis. Read on for more information about hypertrichosis, the werewolf syndrome’s origin, causes, types, and treatments.
What is Hypertrichosis?

Hypertrichosis [1] is a disorder that features strange excess hair growth on a part or every part of the career’s body. This differs from the normal pubic androgen-dependent hair, hair at the axilla, forearms, face, or legs. Also, it is not analogous to hirsutism, which causes abnormal excessive hair growth in women — common to men’s usual hair growth pattern — for instance, the hair that grows under the lower part of a man’s face. Indeed, hypertrichosis, termed werewolf syndrome, can occur in men, women, and children. This werewolf hairy attribute can also emanate from birth (congenital) or later in life (acquired). Studies established that this rare case of hypertrichosis may likely be because of a gene mutation, which makes hair grow beyond the average hair growth in other people. Sometimes, there are severe cases of hypertrichosis, where the hair covers the person from head to toe. Most of these people who suffer significantly from hypertrichosis experience skin irritation, depression, stigmatization, bullying, isolation, low-self esteem, anxiety, and negative attention from people. In addition, people diagnosed with werewolf syndromes lose their social life activities and special events that concern them due to the environment they find themselves in.
Moreover, the recorded cases of werewolf syndrome worldwide are below a hundred since it was discovered in 1642 by Petrus Gonsalvus[2] of the Canary Islands. The hair disorder is not a virus or contagious disease that spreads and may cause health disaster. Nevertheless, people with this syndrome have access to medical and social benefits to living a fulfilled life with their family members.
The Symptoms of Hypertrichosis
The evidence of hypertrichosis is the abnormal appearance of highly excessive hair growth on unusual body parts or all over the body. More so, these unique symptoms are categorized into three different types of hair growth:
Lanugo
Lanugo is the long, thin, fine, and soft hair that covers a baby at birth. This hair covering has no pigment and typically disappears after birth in a few weeks. However, medical practitioners may diagnose hypertrichosis if the lanugo hair on a baby stays longer than expected or continues as the child grows from an infant to a teen.
Vellus
Vellus is characterized by soft and short follicles, which may have pigment or no pigment. Hypertrichosis will make this hair visible on every body part except areas without hair follicles.
Terminal
The terminal is coarse, long, thick, and very dark hair commonly found on the face, axilla, back, and chest of those diagnosed with hypertrichosis.
Types of Hypertrichosis
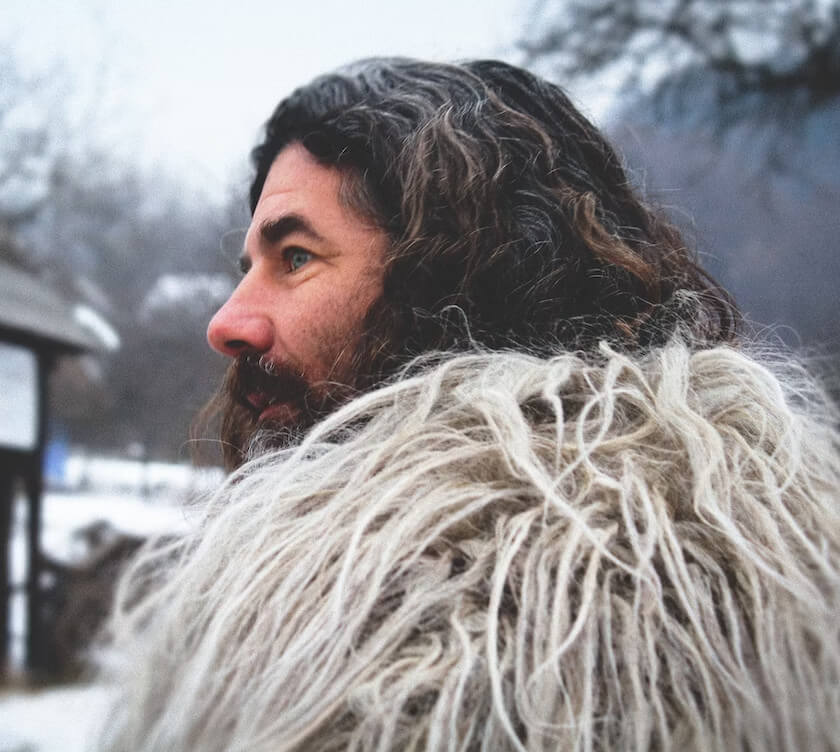

Hypertrichosis types are associated with whether the hair covers the whole body (Generalized hypertrichosis) or a part of the body (Localized hypertrichosis). There are mainly two types, and these are congenital [3] and acquired hypertrichosis.
Congenital Hypertrichosis
This disorder is a type of hypertrichosis from birth in which a child is born with this disorder that his hair refuses to disappear at some certain parts of his body at the expected time.
Types of Congenital Hypertrichosis
Congenital hypertrichosis lanuginose:
This condition becomes evident when the appearance of lanugo refuses to disappear on the baby a few weeks after birth but continues to grow. This disorder tends to appear all over the baby’s body as the child grows unless treated.
Congenital hypertrichosis terminals:
This disorder is confirmed when unusual, very thick, dark, and long hair growth develops after birth and is visible on a newborn child’s body. This hair develops rapidly as the child ages, and it covers every part of his body throughout his lifetime.
Nevoid hypertrichosis
This disorder reveals abnormal bushy hair growth in a particular area of a person’s body. The concentration of such unusual excessive hair is solid and thick on the person’s skin. However, this condition can be ameliorated if the healthcare consultant discovers the cause early.
Hirsutism
This unusual hair growth is most common in women; some people mistakenly consider hirsutism[4] as hypertrichosis. The hair abnormally grows in women primarily due to hormonal imbalance, and it appears where it will appear in men, like the chest, chin, and back.
Acquired hypertrichosis
This type of hypertrichosis occurs in a person as he ages instead of at the beginning of their birth. This disorder can either appear as a generalized or localized kind of hypertrichosis. In addition, hair growth can be lanugo, terminal, or vellus, just like congenital hypertrichosis.
Causes of Hypertrichosis
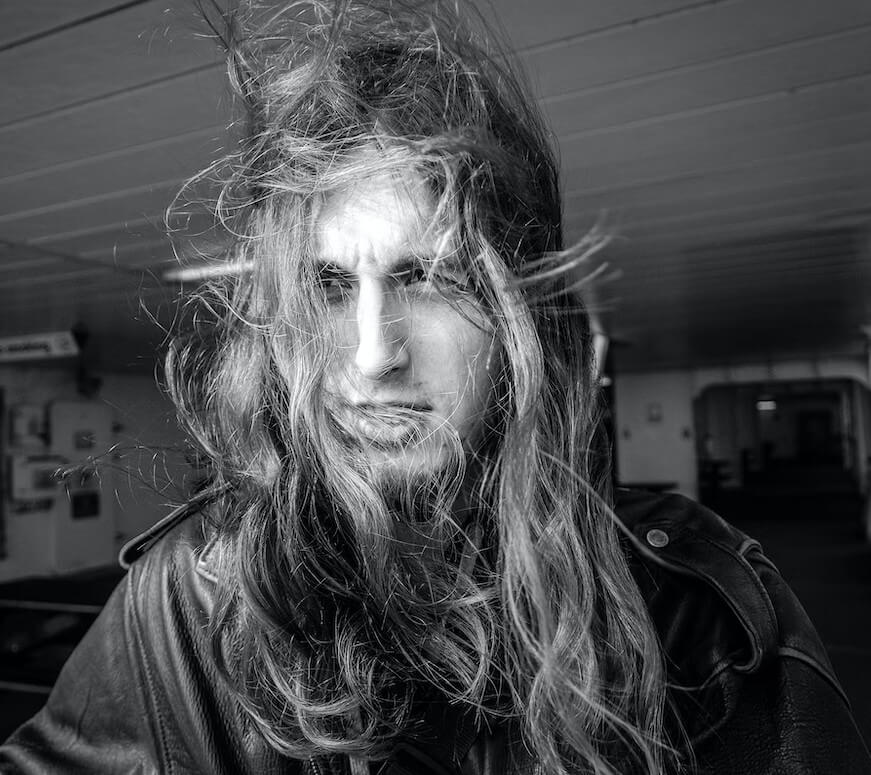

Though studies have not revealed the causes of werewolf syndrome, many medical researchers have tried to discover the root of this disorder. However, only the possible reasons are available for analysis:
Some researchers believe congenital hypertrichosis may be innate to some children or inherited from their lineage. The genes that make hair grow may reactivate themselves in the womb if such symptoms are validated in the family medical history. No concrete source has proved this assumption ultimately to date, though.
Acquired hypertrichosis, unlike congenital hypertrichosis, is likely to occur in a person lately due to some reasons like
- Malignancy: worst medical condition of cells
- Porphyria cutanea tarda: a rare disorder that is full of painful experiences and blistering skin lesions[5] through sunburn
- Malnutrition or eating disorders
- Certain drugs and medications, such as hair growth drugs, photosensitizers, ciclosporin, specific immunosuppressants, anticonvulsants, phenytoin, and androgenic steroids
- Cancer and cell mutation
- HIV/AIDS
- Acromegaly
- Scratching (Lichen simplex)
- POEMS syndrome
- Juvenile hypothyroidism
- Dermatomyositis
- Wrong Application of plaster cast
- Inappropriate use of Minoxidil for hypertension or alopecia
- Vascularity
- Trichomegaly
Diagnosis
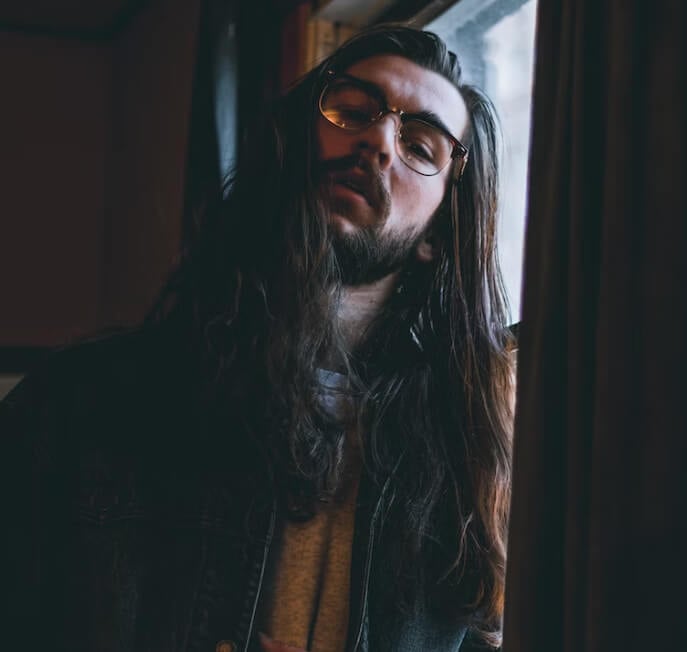

Hypertrichosis has no cure or established solution, especially for people with severe hypertrichosis. It can only be managed or curbed from growing excessively. Professional healthcare providers only need to discover this disorder’s type and the cause after proper diagnosis. A dermatologist or medical doctor can validate this by diagnosing a patient, using a microscope to discover if there is a trait of hypertrichosis.
In the cases of hirsutism, the doctor may run blood tests to confirm the state of hormonal imbalances and know if a hair growth disorder is building up. Also, a genetic test is run to identify mutations in the cases of Cornelia de Lange syndrome and Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome. Imaging tests like ultrasound are cardinal to confirm the presence of hypertrichosis if the doctor diagnoses a patient with cancer.
Treatments
Managing or treating hypertrichosis has different approaches based on the type of hair disorder a patient is diagnosed with.
Avoiding hypertrichosis-causative drugs
Avoiding or minimizing the use of some hypertrichosis-causative drugs like Minoxidil can reduce the manifestation of hair growth disorders at an early stage for an acquired hypertrichosis patient. Most of these drugs are used to treat hypertension, but they have their side effects. You should stop it and consult your medical consultant for a proper check-up.
Short-term Hair Removal
A patient can manage hypertrichosis by removing abnormal hair growth through shaving,
waxing
, plucking, bleaching, or using chemical epilation on the affected area. Though these methods are temporal, you must repeat them until it disappears and not looking odd in society. Notwithstanding, using these short-time methods may trigger pains and irritation in the skin. You should seek the service of a professional dermatologist.
Long-term Hair Remover
Long-time treatments with light hair removal, such as laser, electrolysis, and IPL devices, will long-lastingly target and destroy the appearance of hypertrichosis.
Laser hair removal
will clear every trace of the individual hair follicles with its light. However, it only works better on dark color skin. Electrolysis, on the other hand, uses its heat to destroy all hair follicles, and it works well for dark and white skin. Managing and treating hypertrichosis with intense pulsed light is better and more effective. In addition, it is recommended by the US government for people diagnosed with hypertrichosis only that it requires a lot of money and sessions to see one’s desired results.
Our Final Take
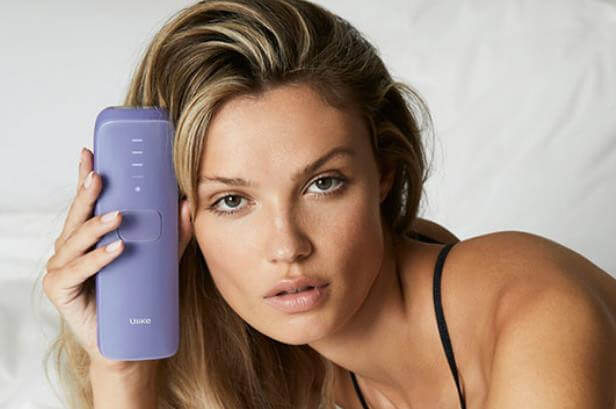

Hypertrichosis is a rare hair disorder that appears excessive and abnormal on its career. It was discovered in the early 19th and 20th centuries. This condition has no established cause unless a professional doctor traces and finds it through diagnosis. People who are carriers of this condition are either born with it (Congenital) or develop this werewolf syndrome later (Acquired) due to the reactions to some medical conditions. Likewise, there is no cure, but healthcare providers can help you manage this abnormal hair growth using manual methods of removing hair, like waxing, plucking, and so on. Other fast hair removal is laser hair removal, topical medication, and electrolysis. We strongly recommend you consult your doctor if you notice this abnormality. Also, consider discussing your family medical history that is related to this strange hair growth or if you discover it on the part of your body (excluding parts of the androgen-dependent hair) during self-examination. Finally, consider one of
Ulike IPL devices
to help remove any unwanted hair or abnormal hair that makes you feel uncomfortable. Our FDA-cleared skin-safe IPLs are pain-free and effective beyond expectation.
References
[1] Hypertrichosis, Saleh D, Yarrarapu SNS, Cook C.
[2] Petrus Gonsalvus And The Real Beauty And The Beast Story By All That’s Interesting | Edited By John Kuroski
[3] Congenital generalized hypertrichosis: the skin as a clue to complex malformation syndromes, Piero Pavone, corresponding author Andrea D. Praticò
[4] Hirsutism Written by Lisa Fields
[5] Cutanea Tarda Porphyria, Shah A, Bhatt H.
4985
.

 By Nancy H, PharmD
By Nancy H, PharmD