Dark spots present on the face can be the result of various
hyperpigmentation disorders
. Getting rid of them can be challenging since not all dark spots are created equally. While it may not be possible to remove them completely for good, they can certainly be improved with the right treatment.
In this article, we will discuss the different causes and types of dark spots and the skincare approach you can follow to get brighter, more even-looking skin.
What are dark spots?
Dark spots appear when certain regions of our skin get “darker” than the rest due to increased production of melanin, the substance responsible for coloring our skin.
Melanin is produced by specialized skin cells known as melanocytes, in a process consisting of different steps, which involve:
1.
Synthesis
of melanin by several enzymes, where
tyrosinase
is of most importance.
2.
Packing
of melanin in granules, which are then
transferred
from melanocytes to the skin cells (keratinocytes) which get then pigmented.
3.
Transport
of the pigmented cells upward during the normal skin cells turnover process, coloring the surface of the skin.
When this pigmentation process is up-regulated due to different triggers, melanin can be overproduced in certain regions of the skin more than others, resulting in what we see as dark spots.

What causes dark spots?
Not all dark spots are created equally since different factors can trigger the overproduction of melanin in the skin. Among the most common causes of dark spots, we can find:
-
Sun exposure:
sunlight is the main factor triggering melanin production. Most dark spots and hyperpigmentation are developed or worsen due to exposure to the sun. -
Hormones:
hormonal imbalances can induce the production of melanin. For instance, some dark spots known as “melasma” can appear during pregnancy or even taking birth control pills [1]. -
Injuries and Inflammation:
Any type of inflammatory skin condition (acne, eczema, psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis) or trauma (a burn or a cut) can cause post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) in the affected area. The most common case is dark spots resulting from acne lesions [1]. -
Age:
As part of the normal aging process, an imbalance in cell turnover and melanin production and distribution can occur, resulting in uneven pigmentation [2]. Cumulative UV exposure during aging also decreases our antioxidant defenses, making the skin more prone to photodamage [3].
Other factors such as underlying health conditions, medications, and even occupational reasons may cause hyperpigmentation as well.
How to get rid of dark spots?
Before undergoing any treatment or purchasing any product, it’s important to determine what caused those dark spots to appear in the first place. Treating the underlying cause first is crucial to removing dark spots effectively. For example, if acne is causing your dark spots, it’s critical to treat this condition first, so it’s best to consult a board-certified dermatologist.
If the primary cause was already treated, overcome, or removed, several skin care products can help improve the appearance of those remaining dark spots. These cosmetics are formulated with various skin-brightening ingredients that act at different stages of the pigmentation process.
However, before explaining these ingredients, we need to stress the fact that no treatment to remove hyperpigmentation will be successful unless you protect yourself from the sun, which is why broad-spectrum sunscreens are a MUST in any skin care regimen for dark spots.
Let’s explore.
1.
Broad-spectrum sunscreens
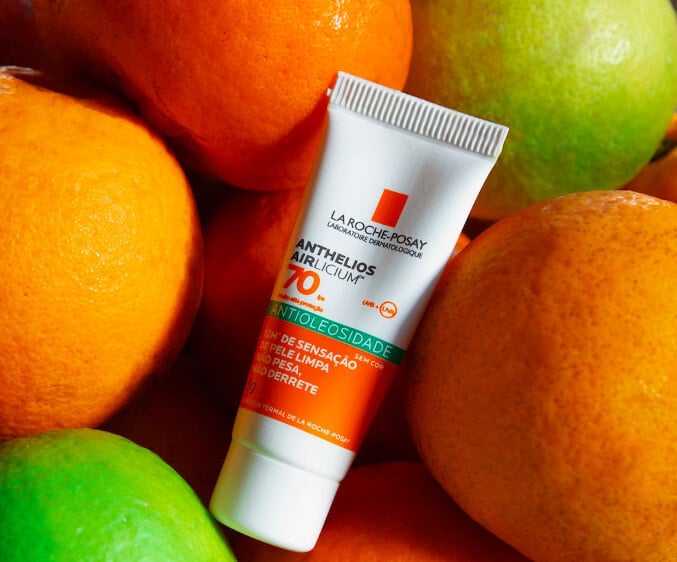

Sunscreens are an essential step in any
skincare routine
, especially when it comes to treating dark spots, since UV rays are the main trigger of melanin production, and hyperpigmented skin is particularly sensitive to sunlight.
Applying sunscreen daily is key to preventing those pigmented spots from getting darker over time and to achieving satisfactory results from any
skin-lightening treatment
.
What do you need?
Choosing the right sunscreen
for your skin is key. Sunscreens with broad spectrum (covering UVB and UVA) with SPF 50 or higher and PA++++ are recommended. You may benefit from the use of tinted sunscreens to cover dark spots as you add photoprotection from visible light that might also contribute to skin darkening [4].
2.
Skin-brightening Ingredients

Using skincare products infused with skin-brightening ingredients that target multiple steps of the pigmentation process can help obtain satisfactory results. According to their mechanism of action, skin-brightening products may contain:
Melanin inhibitors:
Molecules able to
inhibit the enzyme tyrosinase
are used to restrain melanin formation in dark spots. Brightening products often contain the following tyrosinase inhibitors:
- Azelaic acid: in a concentration equal to or below 10% in cosmetics.
- Arbutin: a natural derivative of hydroquinone.
- Tranexamic acid.
- Kojic acid.
-
Vitamin C
.
- Licorice.
Other actives, such as niacinamide – a form of
vitamin B3
– have been demonstrated to block instead the
transfer of melanin granules
to the skin cells [5].
Antioxidant molecules:
Oxidative stress has also been implicated in the pathways that trigger melanin biosynthesis [3]. Therefore, antioxidants capable of neutralizing excess free radicals may contribute to limiting melanin formation.
Among the antioxidant molecules used in skincare, we find the popular
vitamin C
, but also
vitamin E
and licorice.
has also been proven to significantly boost the effectiveness of sunscreens, prolonging, and enhancing their UV protection [6].

Retinol:
Another strategy includes the use of retinol, a
vitamin A
derivative, which stimulates the shedding of old hyperpigmented cells by regulating skin renewal pathways and enhancing the cell turnover process [7]. Retinol may also influence the proper distribution of melanin in the skin [7].
Nonetheless, retinol may irritate the skin, which may limit its use. It’s advisable to start using it at lower concentrations (0.15 – 0.30 %) and then gradually increase the concentration and frequency as tolerated. If your skin is sensitive or doesn’t tolerate retinol at all, or if you are pregnant, retinol can be substituted with its natural alternative,
bakuchiol
.
Chemical exfoliants:
Ingredients such as AHA (alpha hydroxy acids, specifically glycolic acid [8]) and
BHA
(beta hydroxy acids, like salicylic acid) are useful in the treatment of dark spots, specifically to remove the melanin already deposited on the surface of the skin. These molecules act by disrupting the bonds between skin cells, which causes their detachment, thus enhancing the desquamation of old, pigmented skin cells to even out skin tone.
They may also be combined with
exfoliating enzymes
(papain, bromelain) to boost the desquamation process [9].
SKINCARE ROUTINE FOR DARK SPOTS

At this point, you may be wondering what’s the best way to include these ingredients in your
skincare routine
.
We will simplify this for you and give some tips so you can tailor your routine:
– Find products that already combine different skin-brightening ingredients. Most of the brightening products available contain one or more tyrosinase inhibitors (like azelaic acid) combined with niacinamide, licorice, or BHA, for example.
– You can choose 3 products to cover each stage of the pigmentation process: one with melanin inhibitors and antioxidants, a second with chemical exfoliants, and another to boost cell renewal (retinol).
– Always use products as directed. Almost all ingredients mentioned can be used during the day, except for retinol and AHA peels, since they can make your skin sensitive to light.
– Wearing sunscreen daily is essential, so be mindful to
choose a sunscreen
that adapts to your needs.
Now, let’s put these tips into practice.
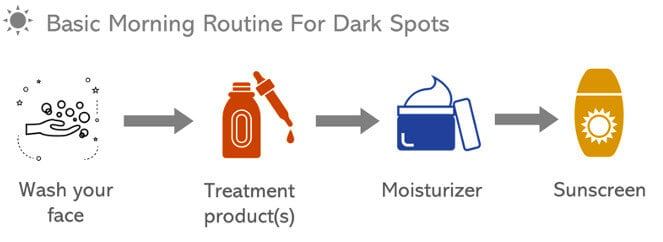
Morning routine
A simple morning routine you can follow can include the next steps:
1.
Wash your face.
2.
Apply the treatment product(s) for dark spots.
Try to include products with several skin brighteners (preferably with vitamin C in them). Some examples:
– Glow Recipe Guava Vitamin C Dark Spot Brightening Treatment Serum, which additionally contains tranexamic acid, ferulic acid, and vitamin E.
– Paula’s Choice 10% Azelaic Acid Booster, with additional BHA and licorice.
3.
Moisturize.
4.
Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen.
Night Routine
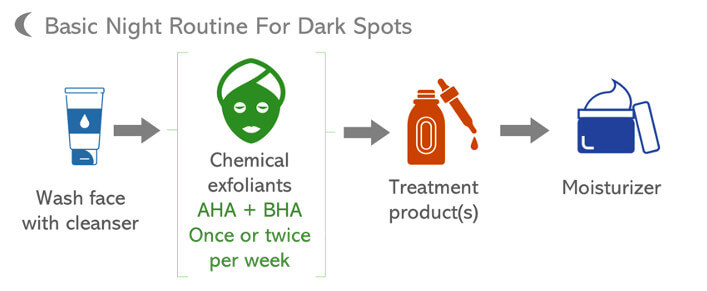
A simple night routine you can follow can include the next steps:
1.
Wash your face with a cleanser.
2.
Exfoliate once or twice per week.
Use an exfoliating mask with AHA, BHA, and/or enzymes. If you have sensitive skin, patch test before, or choose a gentle option to avoid irritation.
3.
Apply the treatment product(s) for dark spots.
You may repeat the morning product and/or add another product with retinol every other night, like CeraVe Resurfacing Retinol Serum.
*Never combine retinol with chemical peels on the same night to avoid irritation.
Sensitive to retinol? Try one with
bakuchiol
like Paula’s Choice CLINICAL Discoloration Repair Serum, which contains tranexamic acid and niacinamide too.
4.
Moisturize.
THE TAKEAWAY
Dark spots give the skin a dull and uneven appearance. Hyperpigmentation, although difficult to treat, can be greatly improved by following the right approach with skin-brightening products. Dark spots won’t disappear overnight, so patience and commitment during treatment are key. Thus, skincare routines take time to fully work and satisfactory results may appear only after weeks or months.
If you don’t see any improvement whatsoever, it is highly recommended that you visit a board-certified dermatologist for advice on the best
skin-lightening treatment
for your hyperpigmentation.
REFERENCES
[1] Nieuweboer-Krobotova, L. (2012). Hyperpigmentation: types, diagnostics and targeted treatment options. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, 27, 2–4. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.12048
[2] Kang, H. G., Lee, J. Y., Papaccio, F., Bellei, B., & Picardo, M. (2021). Alterations of the pigmentation system in the aging process. Pigment Cell & Melanoma Research, 34 (4), 800–813. https://doi.org/10.1111/pcmr.12994
[3] Nahhas, A. F., Abdel-Malek, Z. A., Kohli, I., Braunberger, T. L., Lim, H. W., & Hamzavi, I. H. (2018). The potential role of antioxidants in mitigating skin hyperpigmentation resulting from ultraviolet and visible light‐induced oxidative stress. Photodermatology, Photoimmunology and Photomedicine, 35 (6), 420–428. https://doi.org/10.1111/phpp.12423
[4] Dumbuya, H., Grimes, P. E., Lynch, S. V., Ji, K., Brahmachary, M., Zheng, Q., Bouez, C., & Wangari-Talbot, J. (2020). Impact of Iron-Oxide Containing Formulations Against Visible Light-Induced Skin Pigmentation in Skin of Color Individuals. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology, 19 (7), 712–717. https://doi.org/10.36849/jdd.2020.5032
[5] Wang, Y., Zhao, J., Jiang, L., & Mu, Y. (2021). The Application of Skin Care Product in Melasma Treatment. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology, Volume 14, 1165–1171. https://doi.org/10.2147/ccid.s323748
[6] Telang, P. S. (2013). Vitamin C in dermatology. Indian Dermatology Online Journal, 4 (2), 143. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3673383/
[7] Michalak, M., Pierzak, M., Krecisz, B., & Suliga, E. (2021). Bioactive Compounds for Skin Health: A Review. Nutrients, 13 (1), 203. https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/13/1/203
[8] González-Molina, V. (2022, May 1). Topical Treatments for Melasma and Their Mechanism of Action. PubMed Central (PMC). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9122278/
[9] Trevisol, T. C., Henriques, R. O., Souza, A., & Furigo, A., Junior. (2021). An overview of the use of proteolytic enzymes as exfoliating agents. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 21 (8), 3300–3307. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.14673

 By myulikeadmin
By myulikeadmin



